Ethernet Hardware and basic architecture
A cross section of a Ethernet cable is as shown below –
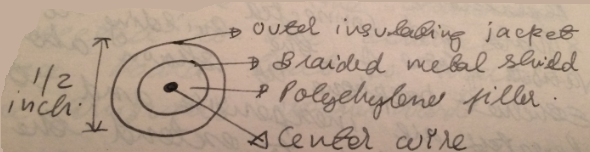
Ethernet is typically a 10Mbps local area packet switched network technology. The cross section of an Ethernet cable is as shown above. The Ethernet coaxial cable is of 1/2 inch in diameter and is extendable upto 500-1500 meters. The outer insulating jacket and braided metal shield prevents interferences and signal disruption. A resistor, polyethylene fills between the central wire and the shield. The cable as a whole is called ether.
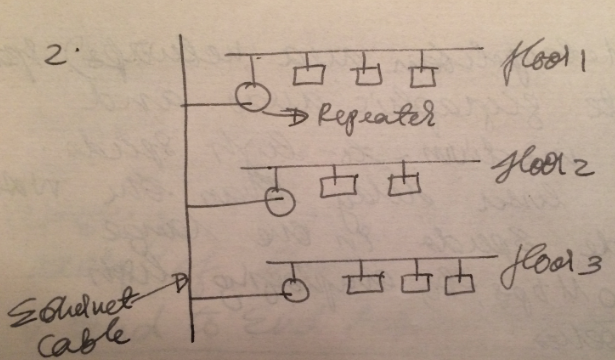
Repeaters may be used along with the ethernets for extending the ethernet signals to longer distances. Repeaters strengthens/amplifies the signals and connects each LAN on the various floors of the building to the Ethernet backbone as shown above. Repeaters are inexpensive and the least costlier method to extend the ethernet. The disadvantage is that they also amplify the noise signal along with the actual signals and they are difficult to be isolated for repair.
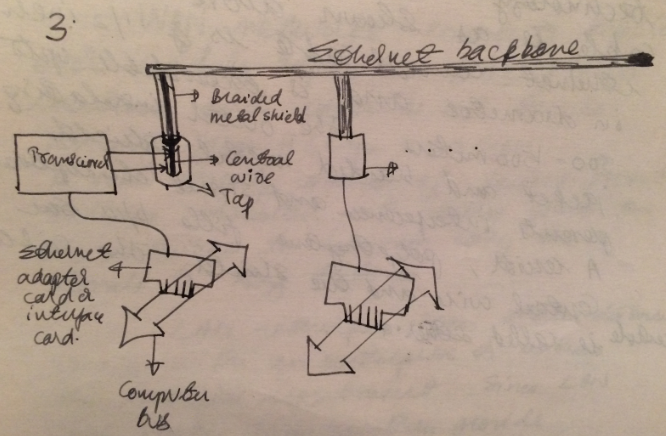
As shown in the figure above, the Ethernet cable is connected to the host computer via the ethernet tap via the host ethernet interface card. As shown, the taps consists of special electronic component called transceiver whose pins cut across in a ‘T’ to touch the central wire and the braided shield of the Ethernet for sensing the signals on the ether cable. The transceiver is connected to the Ethernet interface board that is inserted on the computer’s motherboard.
The Transceiver has a digital circuitry that allows it to communicate with the host computer. It could sense when ether is in user and can translate analog electrical signals on the ether to (and from) digital form. The transceiver cable that runs between the transceiver and host interface carries power to operate the transceiver as well as signals to control its operation.
The Ethernet interface card on the host computer is a set of complex electronic components consisting of a microprocessor for controlling the transfer of signals between the ether and the computer. The Ethernet interface card controls the operation of the transceiver connected to it according to the instructions that it receives from the computer, supports the basic input/output operations while transferring the data signals between ether and the computer, interrupts the transfer when the task has been completed and reports status information.