Graph Traversals and Spanning Forests
Connected Graph
A graph is said to be connected if there is a path between any two of its nodes.
Cycle
A Path from a node to itself is called a Cycle. A rgaph must require at least 3 nodes to form a cycle.
Tree
A Tree is a connected graph without cycles.
Spanning Forests
A Forest may be defined as an acyclic graph which has each nodes having one or no predecessors. A Tree may be defined as a forest in which only one node has no predecessors. A Forest may be a single tree or a collection of trees. A forest is said to be ORDERED if it consists of ordered trees.
A Forest F is said to be a Spanning Forest of a graph G if –
- F is a sub-graph of G containing all nodes of G
- F is an ordered forest consists T1, T2 …… Tn ordered trees
- For some T, of the Spanning Forest F, the nodes contained in it are not contained in some other Tj of the same Spanning Forest.
A Spanning Forest consisting of a single tree is called a Spanning Tree.
Consider a Graph below –
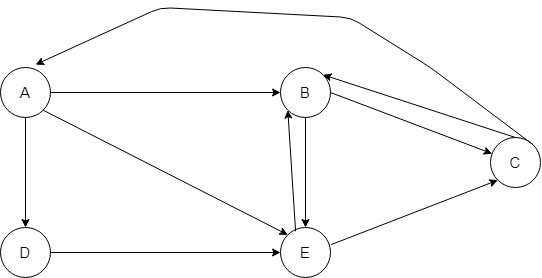
A Spanning Forest could be drawn as shown below –
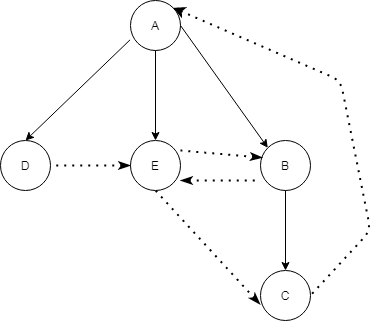
Dotted lines shows the edges in graph not present in Spanning Forest, solid line shows tree edges.
Tree Edges of a graph are edges present both in gaph and Spanning Forest eg: <A, D>, <A, E>, <A, B>, <B, C>.
Forward edges are arcs of the graph from a node to a spanning forest non-son descendant eg: <E,C>
Back Edges are arcs of the graphs from a spanning forest node to an ancestor eg: <CA>
Cross edges are arcs of the graph from a spanning forest node to a non-descendant , non-ancestor node eg: <D,E>, <E,B>, <B,E>